Publications
For an up-to-date list of my research papers, please see my Google Scholar.
arXiv
PhysicsAgentABM: Physics-Guided Generative Agent-Based Modeling
Kavana Venkatesh , Yinhan He , Jundong Li , Jiaming Cui
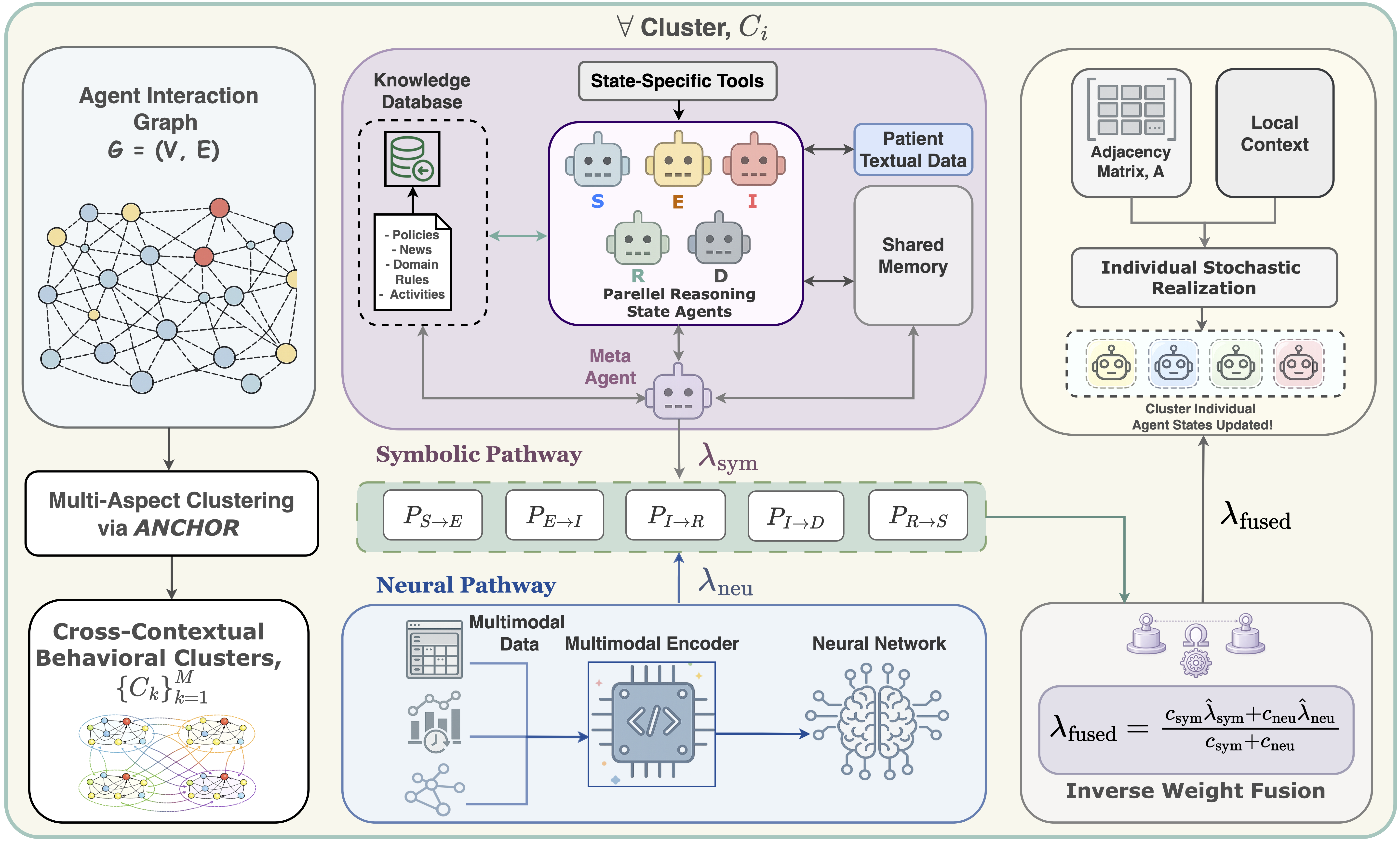
Large language model (LLM)-based multi-agent systems enable expressive agent reasoning but are expensive to scale and poorly calibrated for timestep-aligned state-transition simulation, while classical agent-based models (ABMs) offer interpretability but struggle to integrate rich individual-level signals and non-stationary behaviors. We propose PhysicsAgentABM, which shifts inference to behaviorally coherent agent clusters: state-specialized symbolic agents encode mechanistic transition priors, a multimodal neural transition model captures temporal and interaction dynamics, and uncertainty-aware epistemic fusion yields calibrated cluster-level transition distributions. Individual agents then stochastically realize transitions under local constraints, decoupling population inference from entity-level variability. We further introduce ANCHOR, an LLM agent-driven clustering strategy based on cross-contextual behavioral responses and a novel contrastive loss, reducing LLM calls by up to 6-8 times. Experiments across public health, finance, and social sciences show consistent gains in event-time accuracy and calibration over mechanistic, neural, and LLM baselines. By re-architecting generative ABM around population-level inference with uncertainty-aware neuro-symbolic fusion, PhysicsAgentABM establishes a new paradigm for scalable and calibrated simulation with LLMs.
@misc{venkatesh2026physicsagentabm,
title={PhysicsAgentABM: Physics-Guided Generative Agent-Based Modeling},
author={Kavana Venkatesh and Yinhan He and Jundong Li and Jiaming Cui},
year={2026},
eprint={2602.06030},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2602.06030}
}
arXiv
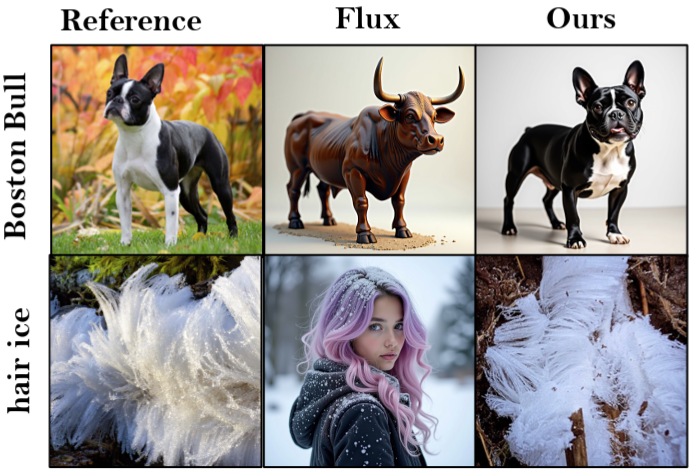
RAVEL: Rare Concept Generation and Editing via Graph-driven Relational Guidance
Kavana Venkatesh , Yusuf Dalva , Ismini Lourentzou , Pinar Yanardag
Despite impressive visual fidelity, current text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models struggle to depict rare, complex, or culturally nuanced concepts due to training data limitations. We introduce RAVEL, a training-free framework that significantly improves rare concept generation, context-driven image editing, and self-correction by integrating graph-based retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) into diffusion pipelines. Unlike prior RAG and LLM-enhanced methods reliant on visual exemplars, static captions or pre-trained knowledge of models, RAVEL leverages structured knowledge graphs to retrieve compositional, symbolic, and relational context, enabling nuanced grounding even in the absence of visual priors. To further refine generation quality, we propose SRD, a novel self-correction module that iteratively updates prompts via multi-aspect alignment feedback, enhancing attribute accuracy, narrative coherence, and semantic fidelity. Our framework is model-agnostic and compatible with leading diffusion models including Stable Diffusion XL, Flux, and DALL-E 3. We conduct extensive evaluations across three newly proposed benchmarks - MythoBench, Rare-Concept-1K, and NovelBench. RAVEL also consistently outperforms SOTA methods across perceptual, alignment, and LLM-as-a-Judge metrics. These results position RAVEL as a robust paradigm for controllable and interpretable T2I generation in long-tail domains.
@misc{venkatesh2025ravelrareconceptgeneration,
title={RAVEL: Rare Concept Generation and Editing via Graph-driven Relational Guidance},
author={Kavana Venkatesh and Yusuf Dalva and Ismini Lourentzou and Pinar Yanardag},
year={2025},
eprint={2412.09614},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.09614},
}
CVPR
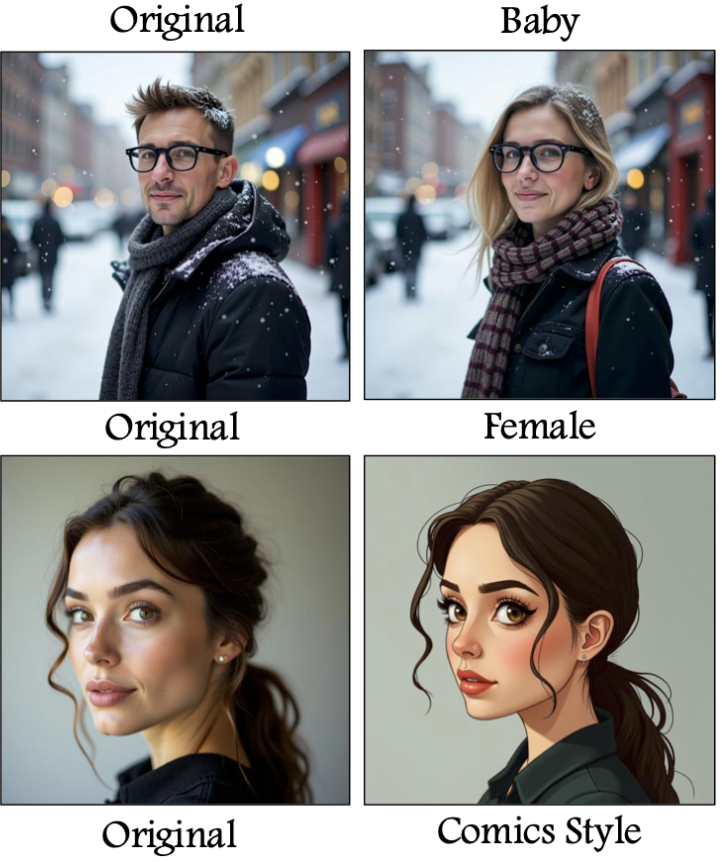
FluxSpace: Disentangled Image Editing in Rectified Flow Models
Yusuf Dalva , Kavana Venkatesh , Pinar Yanardag
Rectified flow models have emerged as a dominant approach in image generation, showcasing impressive capabilities in high-quality image synthesis. However, despite their effectiveness in visual generation, rectified flow models often struggle with disentangled editing of images. This limitation prevents the ability to perform precise, attribute-specific modifications without affecting unrelated aspects of the image. In this paper, we introduce FluxSpace, a domain-agnostic image editing method leveraging a representation space with the ability to control the semantics of images generated by rectified flow transformers, such as Flux. By leveraging the representations learned by the transformer blocks within the rectified flow models, we propose a set of semantically interpretable representations that enable a wide range of image editing tasks, from fine-grained image editing to artistic creation. This work offers a scalable and effective image editing approach, along with its disentanglement capabilities.
@misc{dalva2024fluxspace,
title={FluxSpace: Disentangled Semantic Editing in Rectified Flow Transformers},
author={Yusuf Dalva and Kavana Venkatesh and Pinar Yanardag},
year={2024},
eprint={2412.09611},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}
NeurIPS
CREA: A Collaborative Multi-Agent Framework for Creative Content Generation with Diffusion Models
Kavana Venkatesh* , Connor Dunlop* , Pinar Yanardag
Creativity in AI imagery remains a fundamental challenge, requiring not only the generation of visually compelling content but also the capacity to add novel, expressive, and artistically rich transformations to images. Unlike conventional editing tasks that rely on direct prompt-based modifications, creative image editing demands an autonomous, iterative approach that balances originality, coherence, and artistic intent. To address this, we introduce CREA, a novel multi-agent collaborative framework that mimics the human creative process. Our framework leverages a team of specialized AI agents who dynamically collaborate to conceptualize, generate, critique, and enhance images. Through extensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations, we demonstrate that CREA significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in diversity, semantic alignment, and creative transformation. By structuring creativity as a dynamic, agentic process, CREA redefines the intersection of AI and art, paving the way for autonomous AI-driven artistic exploration, generative design, and human-AI co-creation. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to introduce the task of creative editing.
@misc{venkatesh2025creacollaborativemultiagentframework,
title={CREA: A Collaborative Multi-Agent Framework for Creative Content Generation with Diffusion Models},
author={Kavana Venkatesh and Connor Dunlop and Pinar Yanardag},
year={2025},
eprint={2504.05306},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.05306},
}
NeurIPS
Personalized Image Editing in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models via Collaborative Direct Preference Optimization
Connor Dunlop , Matthew Zheng* , Kavana Venkatesh* , Pinar Yanardag
Text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models have made remarkable strides in generating and editing high-fidelity images from text. Yet, these models remain fundamentally generic, failing to adapt to the nuanced aesthetic preferences of individual users. In this work, we present the first framework for personalized image editing in diffusion models, introducing Collaborative Direct Preference Optimization (C-DPO), a novel method that aligns image edits with user-specific preferences while leveraging collaborative signals from like-minded individuals.
@article{dunlop2025personalized,
title={Personalized Image Editing in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models via Collaborative Direct Preference Optimization},
author={Dunlop, Connor and Zheng, Matthew and Venkatesh, Kavana and Yanardag, Pinar},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2511.05616},
year={2025}
}
IEEE
Fault Analysis and Predictive Maintenance of Induction Motor using Machine Learning
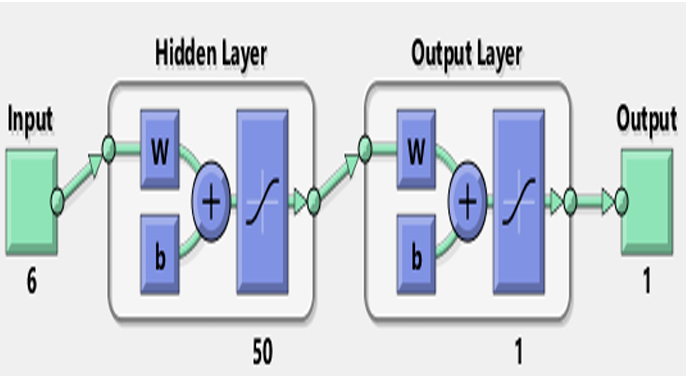
Induction motors are one of the most crucial electrical equipment and are extensively used in industries in a wide range of applications. This paper presents a machine learning model for the fault detection and classification of induction motor faults by using three phase voltages and currents as inputs. The aim of this work is to protect vital electrical components and to prevent abnormal event progression through early detection and diagnosis. This work presents a fast forward artificial neural network model to detect some of the commonly occurring electrical faults like overvoltage, under voltage, single phasing, unbalanced voltage, overload, ground fault. A separate model free monitoring system wherein the motor itself acts like a sensor is presented and the only monitored signals are the input given to the motor. Limits for current and voltage values are set for the faulty and healthy conditions, which is done by a classifier. Real time data from a 0.33 HP induction motor is used to train and test the neural network. The model so developed analyses the voltage and current values given at a particular instant and classifies the data into no fault or the specific fault. The model is then interfaced with a real motor to accurately detect and classify the faults so that further necessary action can be taken.
@inproceedings{Kavana_2018,
title={Fault Analysis and Predictive Maintenance of Induction Motor Using Machine Learning},
url={http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/ICEECCOT43722.2018.9001543},
DOI={10.1109/iceeccot43722.2018.9001543},
booktitle={2018 International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Communication, Computer,
and Optimization Techniques (ICEECCOT)},
publisher={IEEE},
author={Kavana, V and Neethi, M},
year={2018},
month=dec,
pages={963–966}
}